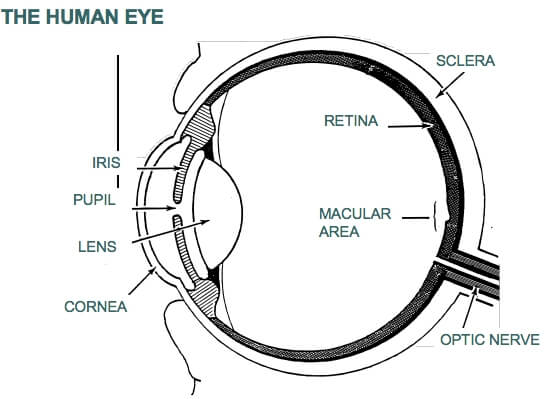
There are several causes of sudden loss of vision. Certain conditions can cause either sudden partial blindness (in which you can detect light and shapes) or sudden complete blindness (when you cannot detect light and cannot see anything). Many of these factors are temporary and can be resolved through timely medical intervention. Some conditions, however, are more serious and are potentially irreversible.
Causes of Sudden Loss of Vision: Partial Blindness
The are several factors that trigger the onset of sudden vision loss in one or both eyes. Here are some of the causes of sudden loss of vision: :
- Migraines (reversible)- These throbbing headaches have time and again reported to cause acute painful vision loss in one or both eyes. They are one of the major causes of temporary blindness in both eyes. The loss of vision caused by migraines is characterized by sensing flashlights or seeing blind spots.
- Retinal Migraine (reversible)- A type of migraine called retinal migraine is sometimes associated with the onset of sudden blindness in one eye. This is called an ‘aura’ and usually affects only one eye. This also causes acute painful vision loss. Once it occurs, the affected individual may lose sight in one of their eyes for about 20 minutes. This can occur right before or even during a migraine.
- Closed-Angle Glaucoma (reversible)- Yet another leading cause of sudden blindness/ temporary blindness in both eyes is closed-angle glaucoma. This condition is mostly associated with loss of vision in just one eye due to excessive pressure caused by a bulging iris. The pressure from the iris prevents drainage of the eye fluid, which, in turn, can lead to a host of different problems like pain in the eye and loss of vision. Permanent vision loss is a possibility if closed-angle glaucoma isn’t diagnosed and treated on time.
- Retinal Vasospasm (reversible)- This condition negatively impacts the flow of blood to the retina. As a result, it may cause a temporary partial loss of vision. Retinal vasospasm causes the blood vessels in your retina to tighten.
- Severe Preeclampsia (reversible) – Sudden vision loss or changes in the vision occur in very serious cases of preeclampsia. Sudden loss of vision can be a sign of something more serious like swelling of the brain or an issue with the central nervous system.
If you experience sudden vision loss during your pregnancy (especially if you have already been diagnosed with preeclampsia), make sure you get medical help immediately.
- Giant Cell Arteritis (potentially irreversible)- Another common cause of temporary vision loss is giant cell arteritis. This condition is a common cause of loss of vision in adults over 50 years of age. If this condition is left untreated, it is known to cause permanent or chronic sudden blindness.
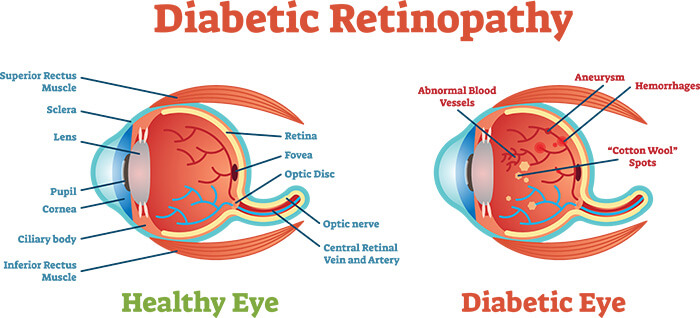
- Retinal Detachment (potentially irreversible) – Retinal detachment is a condition in which the retina moves away from its normal position. When this happens, blood flow to the retinal tissues is blocked, thus, if the condition isn’t treated immediately, it can result in permanent blindness. There are a number of causes of retinal detachment. In diabetic patients, the creation of scar tissue can cause the retina to detach. In some cases, fluid accumulation due to injury can lead to retinal detachment.
Causes of Sudden Loss of Vision: Complete Blindness
- Vitreous Haemorrhage (reversible) – Sudden blindness can also be caused by vitreous hemorrhage where blood leakage occurs. This leakage blocks light and doesn’t allow it to enter the eye, making it difficult for the affected individual to see anything.
- Retinal Vein Occlusion (potentially irreversible) – When the flow of blood to the vein is blocked due to a blood clot or any other factor, it is known as retinal vein occlusion. The blockage of blood supply to the retina can starve the tissues of oxygen and nutrients and is a very serious condition. If left untreated for too long, it can result in permanent blindness.
The conditions mentioned above were some of the most common causes of sudden vision loss. Let us now have a look at some rare causes that may contribute to the onset of sudden blindness. They include:
- Epileptic Seizures (reversible) – While seizures are commonly associated with physical seizures, you may be surprised to know that epileptic seizures can also contribute to sudden blindness in rare cases. About 10 % of people suffering from this condition can have their occipital lobe impacted. This impact can cause loss of vision during or after the seizure.
- Uhthoff Phenomenon (reversible) – This is another rare cause of sudden vision loss. It often affects those who have multiple sclerosis. Some individuals may experience an increase in their body temperature due to multiple sclerosis, causing them to become temporarily blind in one or both eyes.
FAQs:
Q1. What is Amaurosis Fugax?
Amaurosis Fugax is a medical condition that causes an individual to lose eyesight in one or both the eyes due to a lack of blood flow. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as blood clots or lack of blood flow to the blood vessels present in the eye. The Amaurosis fugax differential diagnosis may help in identifying damage and blockages of the blood vessels in the eye that causes sudden loss of vision in one eye.
Q2. Can migraines cause a temporary partial loss of vision in one eye?
Yes, migraines are the number one cause of sudden vision loss in one or both eyes for many. It usually leads to temporary loss of vision in one eye that is characterized by sensing flashlights or sighting blind spots. Blindness triggered by migraines can occur right before or even during a migraine.
Q3. What are the causes of sudden vision loss in child?
The causes of sudden vision loss in children is similar to that in adults. Migraines, blood clots, retinal vein occlusion, and seizures are associated with loss of vision in children just like in adults. Additionally, poor nutrition, inadequate prenatal care, premature birth, and a family history of sudden blindness can also trigger a sudden vision loss.
Q4. How do individuals battling epileptic seizures develop sudden vision loss?
About 10% of the individuals suffering from epileptic seizures develop problems within the occipital lobe. These issues are known to result in sudden blindness in some of the affected people. The onset of sudden vision loss may occur during or after a seizure.
Q5. What is the most common cause of sudden vision loss?
The most common cause of sudden blindness is a migraine headache. These throbbing headaches are reported to cause vision loss in one or both eyes. They are one of the main causes of temporary partial vision loss. The loss of vision caused by migraines is characterized by sensing flashlights or seeing blind spots. Other common causes of sudden vision loss include giant cell arteritis, retinal vasospasm, closed-angle glaucoma, and vitreous hemorrhage.
Q6. How do blood clots cause sudden blindness?
The formation of a blood clot can cause sudden temporary loss of vision in one eye or both eyes. If the required treatment is not availed in time, this condition may result in permanent loss of vision. The clot can either develop in the retinal artery or any other blood vessel, which goes on to cloud your vision and eventually leads to complete loss of vision.
Q7. What is vitreous hemorrhage?
Vitreous hemorrhage is a condition where blood leakage occurs in the eye. This leakage causes blockage of light and doesn’t allow it to enter the cornea, making it difficult for the affected individual to see clearly.
Summary:
Sudden vision loss may have several underlying causes such as various health conditions (migraines, Giant Cell Arteries, Closed Angle Glaucoma, Vitreous Hemorrhage, etc. Loss of vision may also be attributed to reduced blood flow, blood clots in arteries, and more.
Get tested by consulting a top ophthalmologist on MFine to know the causes of sudden loss of vision!
 Gynecologist
Gynecologist General Physician
General Physician Orthopedician
Orthopedician Dietitian
Dietitian Pediatrician
Pediatrician Dermatologist
Dermatologist Psychiatrist
Psychiatrist Andrologist
Andrologist Diabetologist
Diabetologist Urologist
Urologist Gastroenterologist
Gastroenterologist General Surgeon
General Surgeon Endocrinologist
Endocrinologist Dentist
Dentist Cardiologist
Cardiologist Pulmonologist
Pulmonologist Fertility Specialist
Fertility Specialist Oncologist
Oncologist Neurosurgeon
Neurosurgeon Nephrologist
Nephrologist Neurologist
Neurologist Sports Medicine
Sports Medicine Cosmetologist
Cosmetologist